Files and processes
Computer program consists of certain sets of files. Whenever you start a program you launch an executable file which is responsible for running the program. At the same moment the code of executable loads into computer’s memory. This code is called a process. Basically, processes represent the whole application and once you terminate the process, the program doesn’t load.
Viruses, spyware and all other parasites are also programs, so naturally, if you want to stop the activity of a parasite you have to terminate its processes, first. The difference between the processes of a regular program and parasite is that the processes of a parasite are run without user’s consent. That is why it becomes a challenge to terminate these processes.
The running processes are displayed in Windows Task Manger. Unfortunately, some processes of parasites are hidden from you. That’s why you need to use certain methods in order to make your system display such processes.
Below you will find the methods described that can be used for manual termination of processes. These instructions also explain how to find “invisible” files and remove them from the system.
1. How to find and terminate malicious processes?
In order to open Windows Task Manager, press CTRL+ALT+DEL or CTRL+SHIFT+ESC. You can also press Start button and choose Run… option. Then type in taskmgr and press OK.
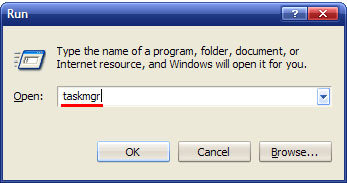
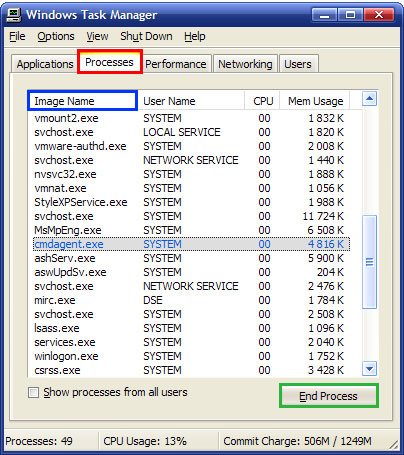
When you see Windows Task Manager screen, choose Processes button and you will see a list of processes running on your system. Click on the Image name button to display the tasks by name. Then find the process needed and click End Process. This way you will terminate the process.
2. Locating and deleting malicious files
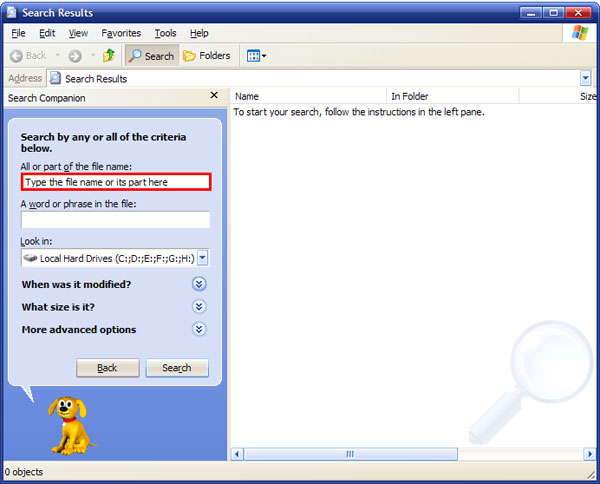
If you know a full name or at least a part of the name of the file you can easily find it using Windows default search tool: Start > Search > For Files and Folders. Type in the file name and select the folders you want to search. In case you don’t know when the file is placed, choose Look in: Local Hard Drives or Look in: My Computer. The file will be displayed in the search results.
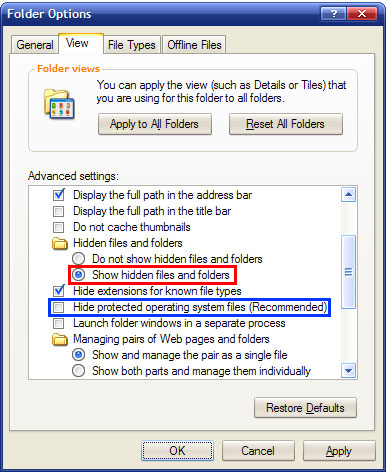
If you are not aware of the file name but you know its possible placement you can try to look for it manually. Before that you must enable displaying hidden and system protected files. Open My Computer, choose Tools menu and click on Folder Options.
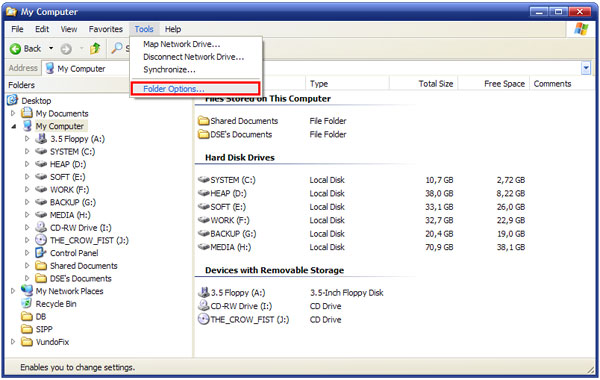
Once in the Folder Options, choose View and select Show hidden files and folders in the Advanced settings list. Then unselect Hide protected operating system files (Recommended).
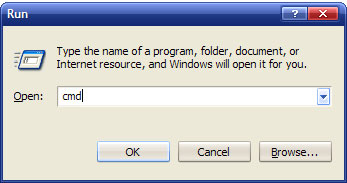
To see the files that are still invisible launch the Command Prompt. Click on Start, choose Run… and type in cmd. Finally press OK.
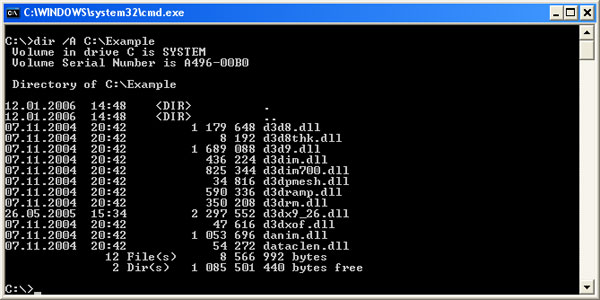
Type in dir /A name_of_the_folder to the console. Then you will see a list of files including hidden ones.
Delete the files needed and then empty the Recycle Bin. In case you receive a message stating that the file cannot be removed because it is in use, go to Windows Task Manager and terminate the corresponding processes.
Unfortunately, some processes might run again right after you terminate them. Then you have to restart your computer in Safe Mode and remove any file needed. Safe Mode doesn’t allow the programs to be run automatically.
3. Pocket KillBox
Computer hackers are improving their creations every day so sometimes it’s difficult to remove certain files even in Safe Mode. Some parasites have rootkits integrated or use some other techniques to protect the files from being terminated by Windows Task Manager and being removed. In this case, the best solution is downloading Pocket KillBox.
The program can be downloaded from its official website.
Run Pocket KillBox, type in the full path of file to delete select Standart File Kill option and click Delete file (a cross next to full path of file to delete).
If that doesn’t work, try deleting the file once again but this time, select Delete on Reboot option. The program will delete the file once you reboot the system.
If none of the described methods are working for you, we highly recommend consulting our technicians on your issue.







